INTEGRATED PHOTONIC BIOSENSOR WITH LAYER DISCRIMINATION CAPABILITY AND COHERENT READOUT, DEVICE, ASSEMBLY AND METHODS ASSOCIATED THEREWITH
Description
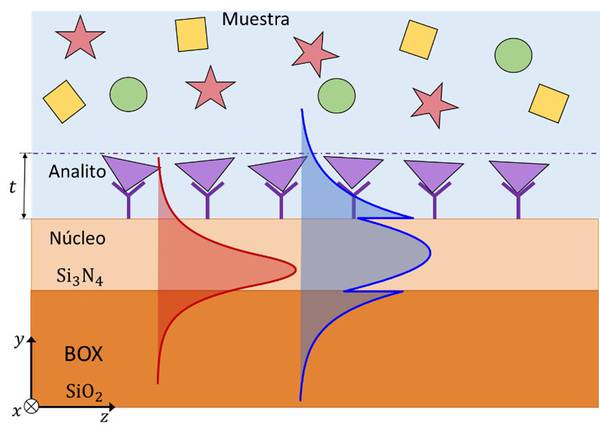
The development of photonic biosensors has been growing in recent years due to their numerous applications: diagnosis of diseases, environmental monitoring or quality control in the food industry. Thus, these devices must ensure reliable, simple and fast detection without the need for instrumentation or qualified personnel. The current trend is to develop point-of-care photonic biosensors integrated on a chip, which do not require labelling (‘label-free’). A layer of biological receptors is applied to the surface of these devices to capture the target analyte when the sample flows over it through a microfluidic channel. This interaction creates an analyte layer, which is detected by the evanescent field of the mode propagating through the waveguide. However, while the protein layers of interest are typically less than 10 nm thick, the penetration depth of the evanescent field exceeds 100 nm. Consequently, the field may also detect minor refractive index variations caused by other components in the sample or by temperature fluctuations, leading to potential errors or false-positive results.
This invention addresses the challenges outlined above by introducing, as its primary feature, a novel Mach-Zehnder-type interferometric architecture with coherent detection. This design enables the discrimination of multiple layers within the cover by utilizing two or more orthogonal states of light with different penetration depths. By propagating two polarizations along the same physical path, the device achieves two independent but simultaneous phase shift measurements over time, eliminating the ambiguities existing in conventional interferometric systems. Additionally, the invention includes various adaptable devices that allow the system to support modes of different orders, operate at multiple wavelengths, or a combination of any of them.
Advantages
The new photonic biosensor offers several notable advantages. Firstly, it preserves the benefits of conventional interferometric systems, including their simplicity and high sensitivity for detecting extremely low analyte concentrations.
Secondly, it supports the simultaneous propagation of two or more orthogonal modes or light states. This allows for multiple independent measurements, providing additional information such as variations in the refractive index across different regions in the cover or the adhered layer thickness.
The third advantage is that the system is low-cost, integrated, and miniaturized. The components used to multiplex different light states are directly coupled into the sensing and reference waveguides, enhancing stability and reducing the complexity of the external equipment required to properly read the signals.
The fourth advantage is that it allows accurate phase detection while avoiding ambiguity and desensitization.
Uses and Applications
The invention could have a huge impact in sectors where molecular detection and interaction are important. A biosensor with layer discrimination capability allows differentiation and analysis of surface phenomena, distinguishing it from other interfering interactions or temperature fluctuations that may lead to erroneous detection.
This feature is especially important in biomedical diagnostics, allowing the detection of very small concentrations of certain biomarkers in order to diagnose diseases in their earliest stages.
Keywords
Sectors
Areas
Patent Number
ES2975382B2 Expediente
Applicants
UNIVERSIDAD DE MÁLAGA
Inventors
ANA SÁNCHEZ RAMÍREZ, IÑIGO MOLINA FERNANDEZ, RAFAEL GODOY RUBIO, JUAN GONZALO WANGUEMERT PEREZ, ROBERT HALIR , ALEJANDRO ORTEGA MOÑUX
Filing Date
16/11/2022
Protection Level: National (Spain) and international
Processing Status: Spanish patent and international protection application